Anthracite is basically another way of saying “hard coal,” just as lignite is another term for “brown coal.”
In contrast to brown coal, hard coal is more compact with higher energy content, which make it affordable to ship around the world. Hard coal is generally what we imagine as a “lump” of coal. Brown coal is softer. But in practice, there is no clear distinction between lignite and anthracite, which are perhaps best seen as two ranges on a spectrum. Indeed, most of the coal used in the United States is called “bituminous” and has a slightly lower energy content than what Germans would call hard coal.
Hard coal in Germany
Coal mining was an important part of Germany’s history. The beginning of the European Union is rooted in the European Coal and Steel Community, which created a common market between Germany and France.
Coal was an important part of Germany’s economic transformation after World War II and provided many jobs in West Germany: for example, in 1956, 125 million tons of hard coal were mined in one year. The coal industry has received billions of euros of subsidies; however, the coal that is now left in the German reserves is now too difficult to mine.
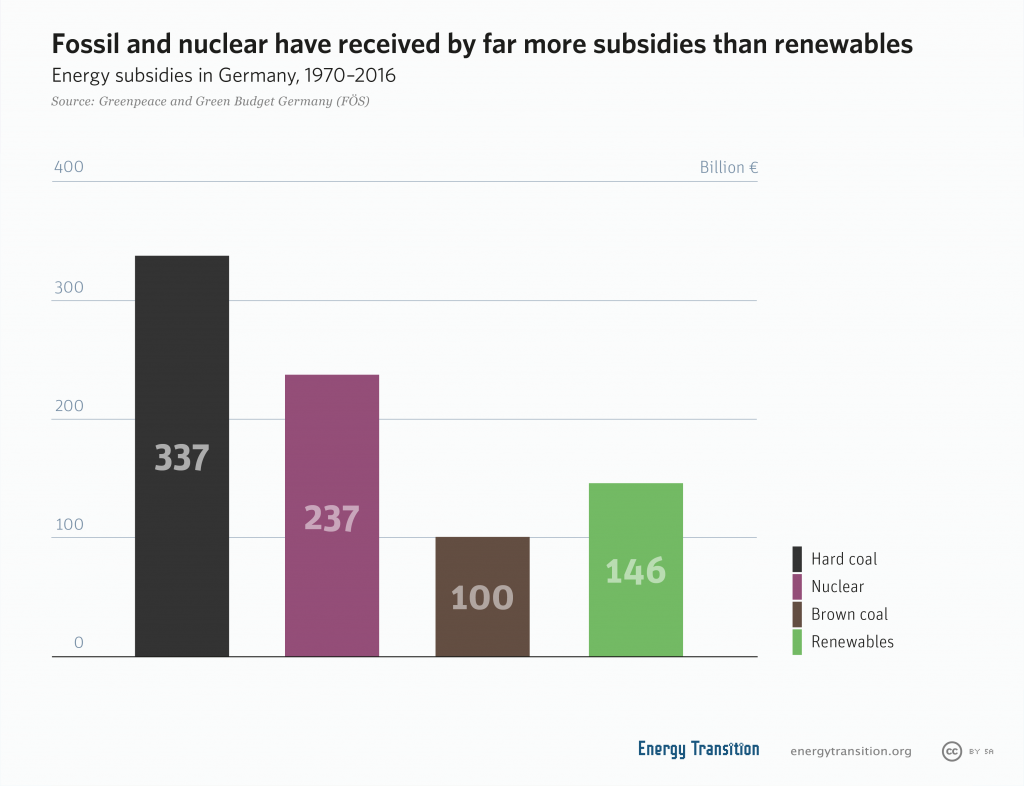
Germany ended mining of hard coal in 2018 (unfortunately, probably for financial and not environmental reasons). The last two hard coal plants in Germany, Prosper-Haniel and Ibbenbüren, closed in 2018. In the last year before their closure, they produced 3.9 million tons of coal. In the EU hard coal production is declining overall, and in 2017 about 80.7 million tons of hard coal were mined.
However, Germany is still burning hard coal in its power plants. In 2016, Germany imported 53 mt of hard coal, or about 4 percent of the world’s total supply. However, this may not last long, as renewables are pushing out coal. In June 2017, the monthly electricity production of PV systems was higher than that of hard coal power plants.
List of hard coal power plants in Germany
Data via the German environmental agency (Umwelt Bundesamt), last updated 2018.
| Power Plant name | Owner | City | Capacity (MW) | District heat (MW) | Year Built (Renovated) |
| Altbach/Deizisau HKW 1 | EnBW Kraftwerke AG | Altbach | 476 | 280 | 1985 (2006) |
| Altbach/Deizisau HKW 2 | EnBW Kraftwerke AG | Altbach | 379 | 280 | 1997 (2012) |
| Bergkamen A | RWE Power AG / Steag GmbH | Bergkamen | 780 | 20 | 1981 |
| Berlin-Moabit A | Vattenfall Europe GmbH | Berlin | 100 | 136 | 1969 (1990) |
| Berlin-Reuter C | Vattenfall Europe GmbH | Berlin | 132 | 244 | 1969 |
| Berlin-Reuter-West D | Vattenfall Europe GmbH | Berlin | 300 | 363 | 1987 |
| Berlin-Reuter-West E | Vattenfall Europe GmbH | Berlin | 300 | 363 | 1988 |
| Bexbach | Steag Power Saar GmbH | Bexbach | 780 | 1983 | |
| Bremen-Farge | Engie Deutschland AG | Bremen | 397 | 26 | 1969 (2007) |
| Bremen-Hafen 6, (Elfi) | swb Erzeugung GmbH | Bremen | 315 | 39 | 1979 |
| Bremen-Hastedt 15 | swb Erzeugung GmbH | Bremen | 130 | 150 | 1989 |
| Duisburg-Walsum 9 | Steag GmbH | Duisburg | 410 | 295 | 1988 |
| Duisburg-Walsum 10 | Steag GmbH | Duisburg | 790 | n.b. | 2013 |
| Frankfurt-West 2 u. 3 | Mainova AG | Frankfurt / M. | 144 | 210 | 1989 |
| Gelsenkirchen-Scholven B | Uniper SE | Gelsenkirchen | 370 | 1968 | |
| Gelsenkirchen-Scholven C | Uniper SE | Gelsenkirchen | 370 | 1969 | |
| Gersteinwerk K2 (DT) (Werne) | RWE Power AG | Werne/Lippe | 665.5 | 1984 | |
| Hamburg-Moorburg A | Vattenfall Europe GmbH | Hamburg | 827 | 120 | 2015 |
| Hamburg-Moorburg B | Vattenfall Europe GmbH | Hamburg | 827 | 120 | 2015 |
| Hamburg-Tiefstack HKW | Vattenfall Europe GmbH | Hamburg | 205 | 785 | 1993 |
| Hannover-Stöcken | Enercity (StW Hannover), Continental, VWK | Hannover | 300 | 425 | 1989 |
| Heilbronn 5 | EnBW Kraftwerke AG | Heilbronn | 125 | 28 | 1965 (2010) |
| Heilbronn 6 | EnBW Kraftwerke AG | Heilbronn | 125 | 28 | 1966 (2010) |
| Heilbronn 7 | EnBW Kraftwerke AG | Heilbronn | 816 | 550 | 1985 (2009) |
| Herne 4 | Steag GmbH / StW Herne | Herne | 511 | 550 | 1989 (2013) |
| Heyden | Uniper SE | Petershagen | 923 | 1987 | |
| Ibbenbüren | RWE Power AG | Ibbenbüren | 838 | 20 | 1985 (2009) |
| Karlsruhe-RDK 7 | EnBW (Rheinhafen) | Karlsruhe | 550 | 220 | 1985 (2005) |
| Karlsruhe-RDK 8 | EnBW (Rheinhafen) | Karlsruhe | 912 | 220 | 2014 |
| Kiel-Ost (GKK) | Gemeinschaftskraftwerk Kiel GmbH | Kiel | 354 | 295 | 1970 (1992) |
| Lünen 6 | Steag GmbH | Lünen | 170 | 1963 (1996) | |
| Lünen 7 | Steag GmbH | Lünen | 350 | n.b. | 1970 (1997) |
| Lünen Stummhafen | Trianel Kohlekraftwerk Lünen GmbH | Lünen | 820 | 35 | 2013 |
| Mannheim 6 | GKM | Mannheim | 280 | n.b. | 1975 (2005) |
| Mannheim 7 | GKM | Mannheim | 475 | 500 | 1983 |
| Mannheim 8 | GKM | Mannheim | 480 | 500 | 1993 |
| Mannheim 9 | GKM | Mannheim | 911 | 500 | 2015 |
| Mehrum 3 (C) | Kraftwerk Mehrum GmbH / EPH | Hohenhameln | 750 | n.b. | 1979 (2003) |
| München-Nord 2 | StW München | Unterföhring | 365 | 550 | 1991 |
| Quierschied-Weiher | Steag Power Saar GmbH | Quierschied | 724 | 30 | 1976 |
| Rostock | KNG mbH | Rostock | 553 | 150 | 1994 |
| Staudinger 5 (Großkrotzenburg) | Uniper SE | Großkrotzenburg | 553 | 300 | 1992 |
| Völklingen-Fenne HKV | Steag Power Saar GmbH | Völklingen-Fenne | 233 | 185 | 1989 |
| Völklingen-Fenne MKV | Steag Power Saar GmbH | Völklingen-Fenne | 233 | 210 | 1982 |
| Walheim 1 | EnBW Kraftwerke AG | Walheim | 107 | 1965 (2011) | |
| Walheim 2 | EnBW Kraftwerke AG | Walheim | 160 | 1967 (2011) | |
| Wedel 1 | Vattenfall Europe GmbH | Wedel | 151 | 423 | 1988 (1993) |
| Wedel 2 | Vattenfall Europe GmbH | Wedel | 138.7 | 1989 (1993) | |
| Westfalen E (Hamm-Uentrop) | RWE Generation SE | Hamm-Uentrop | 820 | 2014 | |
| Wilhelmshaven (Uniper) | Uniper SE | Wilhelmshaven | 788.1 | 1976 | |
| Wilhelmshaven (Engie) | Engie Deutschland AG / BKW FMB Energie | Wilhelmshaven | 830 | 2015 | |
| Wolfsburg Nord A+B | VW Kraftwerk GmbH | Wolfsburg | 140 | 755 | 1959 (2000) |
| Wolfsburg West 10 | VW Kraftwerk GmbH | Wolfsburg | 153 | 130 | 1985 |
| Wolfsburg West 20 | VW Kraftwerk GmbH | Wolfsburg | 153 | 130 | 1985 |
| Zolling-Leininger 5 | Engie Deutschland AG | Zolling | 474 | 150 | 1986 (2011) |